Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
Functional and Bioactive SC21 EV’s
Extracellular Vesicles contain biomolecules, such as RNA, proteins, lipids and carbohydrates, which play an important role in cell communication.
Recent findings have ignited huge interest in EVs for their role in intercellular communication, pathogenesis, and as possible reservoirs of biomarkers. This system has been referred to as the Bio-internet, a cellular information exchange system.
SC21 lab studies the effect of extracellular vesicles on immunomodulation, regeneration pathways, and uses novel methods for extracellular vesicle isolation from cell cultures and biological fluids.
EVs provide a new era of cellular-derived therapies in a cell-free-cell therapy manner.
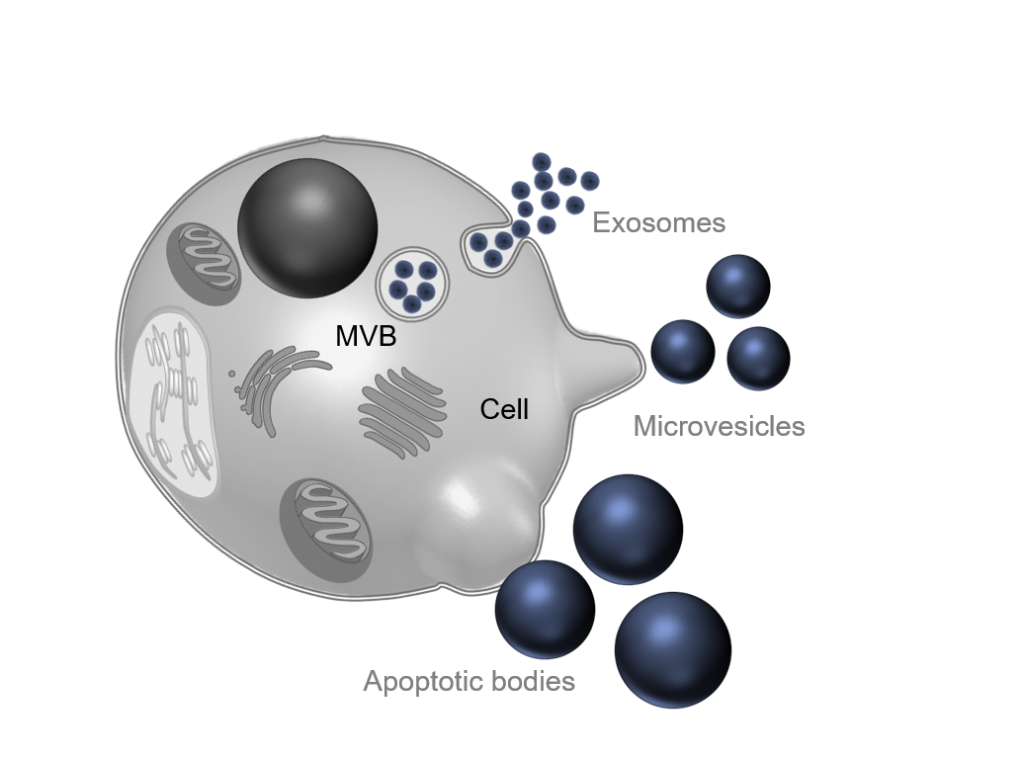
What are Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular Vesicles are composed of three major classes :
- Exosomes (30 – 100 nm) originating from multi vesicular bodies (MVB).
- Microvesicles (100-500 nm) directly bud from the plasma membrane.
- Apoptotic bodies (500 nm – 5µm) are a population of extracellular vesicles secreted during cell death by apoptosis.
The biological function of EVs is to maintain cellular and tissue homeostasis by transferring critical biological cargos to distal or neighbouring recipient cells.
The use of extracellular vesicles (EVs) as cell-free therapy is a promising approach to stimulate tissue regeneration, immunomodulation, and neuroprotection.
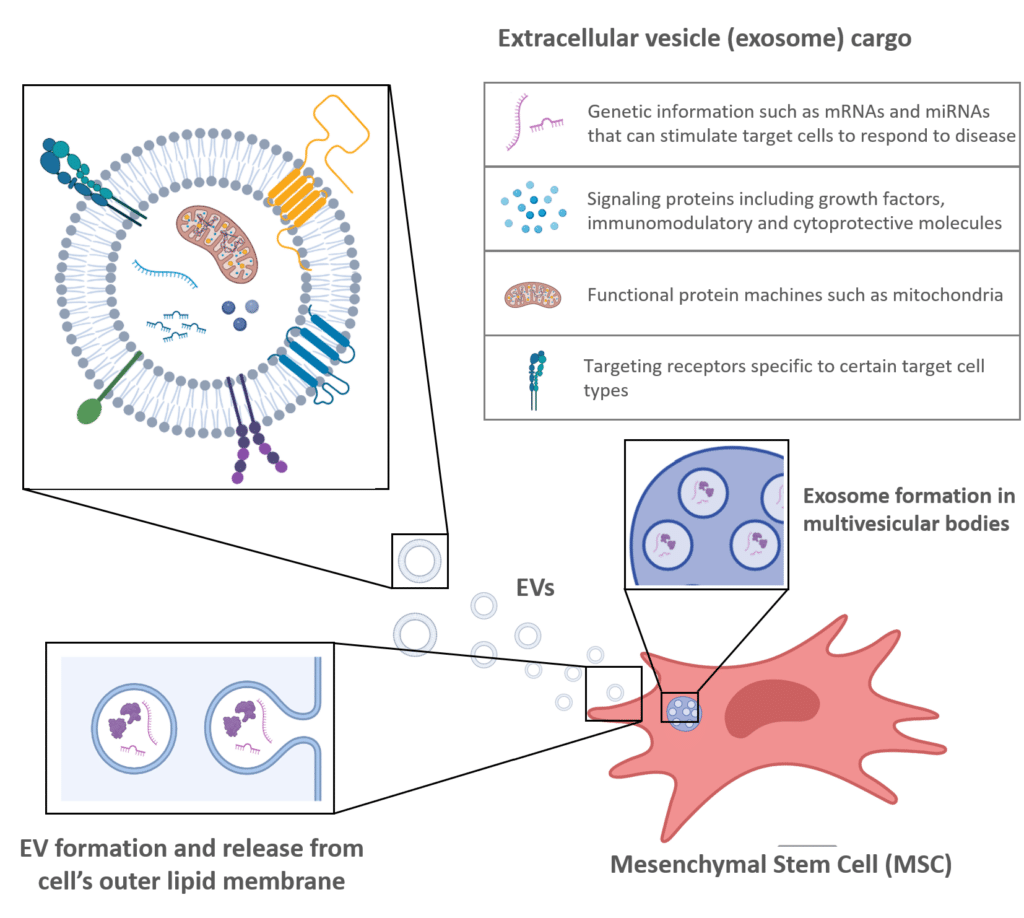
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles and Exosomes
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) have diverse potential to combat disease and regenerate our body’s organs and tissues. But a little understood mechanism is that ~80% of MSC function happens via signaling, stimulating your own body’s cells to mobilize regeneration or responses to disease.
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, have emerged as one of the key players in MSCs’ therapeutic effect. Via specific surface receptors EVs can target specific cell types and deliver cargo into the target cell including signaling molecules, genetic information like miRNAs that can regulate many other genes, mRNAs that can be directly converted inside the target cell into important proteins, or even new mitochondria to help cells renew efficient energy production
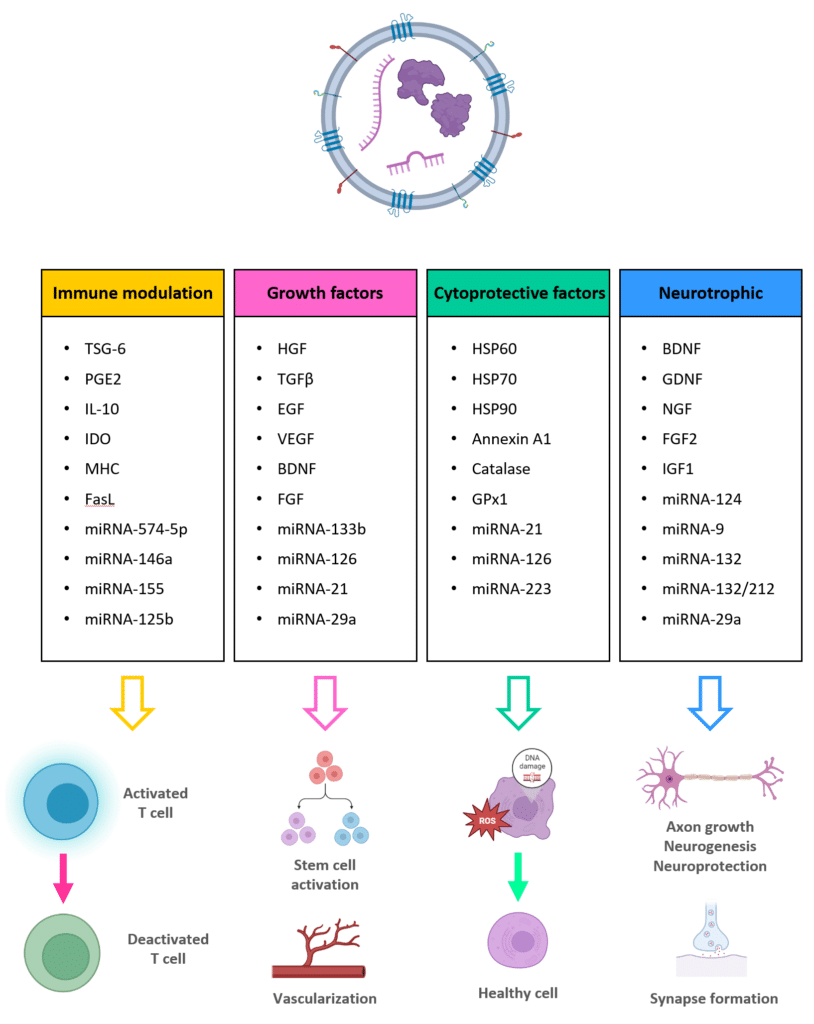
Extracellular Vesicles and Exosomes in Disease Treatments
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) derived Extracellular Vesicles and exosomes have potential in a wide range of diseases.
The therapeutic functions of EVs can be split into several broad categories as listed below:
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles (MSC-EVs)